Openerp sets the stage for modern business management, revolutionizing how enterprises operate with its comprehensive suite of tools. With its roots tracing back to the early 2000s, Openerp has grown into a robust platform that integrates various business processes, from accounting to inventory management, all while being customizable to meet unique organizational needs.
This platform boasts a modular architecture, allowing businesses to tailor their systems with core features that enhance productivity and efficiency. As we dive into its implementation, modules, and user support, Openerp showcases its versatility and reliability in the ever-evolving landscape of business solutions.
Overview of OpenERP
OpenERP, now known as Odoo, has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially launched in 2005 under the name TinyERP, it was designed to be a simple yet powerful resource planning tool. Over the years, it has undergone various transformations, culminating in a comprehensive suite of business applications that cater to various organizational needs. This evolution reflects the changing landscape of business processes and technology, making OpenERP a pivotal player in the ERP market.
The core features of OpenERP encompass a wide range of functionalities that facilitate effective business management. These features include customer relationship management (CRM), sales management, project management, inventory management, and accounting, among others. Each module is designed to be user-friendly and integrates seamlessly with other applications, providing a holistic view of the organization’s operations. This modular approach allows businesses to tailor the software to their specific needs, enhancing operational efficiency.
History and Evolution of OpenERP
OpenERP began as a project aimed at providing an affordable and accessible ERP solution for small to medium-sized enterprises. As it grew in popularity, the platform expanded its capabilities, adding new modules and features to keep pace with the needs of its users. The rebranding to Odoo in 2014 marked a significant turning point, reflecting a broader vision to integrate applications beyond traditional ERP functionalities. This transition included a focus on a more intuitive user interface and enhanced user experience, making it appealing to a wider audience.
Core Features of OpenERP
OpenERP is structured around various core features that are essential for modern business operations. The following list details some of the most prominent features available:
- Comprehensive CRM: OpenERP provides tools for managing customer interactions and relationships, facilitating better communication and customer satisfaction.
- Sales Management: The platform offers functionalities to manage the entire sales process, from quotes to invoicing, improving sales efficiency.
- Inventory Management: OpenERP includes robust inventory tracking features that help businesses manage stock levels, orders, and deliveries effectively.
- Project Management: The integrated project management module allows for tracking progress, deadlines, and resources, ensuring projects are completed efficiently.
- Accounting and Finance: With built-in accounting features, OpenERP helps businesses handle financial transactions, budgeting, and reporting, ensuring compliance and accuracy.
Architecture of OpenERP
The architecture of OpenERP is designed to be modular, allowing businesses to customize their instance according to specific requirements. At its core, OpenERP consists of several key components that work together:
- Database Layer: OpenERP utilizes a PostgreSQL database to manage data storage and retrieval, ensuring reliability and scalability.
- Application Layer: This layer contains the business logic, written primarily in Python, which processes requests and manages user interactions.
- Web Layer: OpenERP’s web interface is built using XML-RPC and JSON-RPC protocols, enabling easy access from any web browser, which enhances user accessibility.
- Client Layer: Users interact with OpenERP through a web client, providing a user-friendly interface that simplifies navigation and task management.
“OpenERP’s architecture ensures that each module operates independently, promoting flexibility and scalability for businesses of all sizes.”
The robust architecture supports a wide variety of integrations with third-party applications, enabling organizations to extend functionality as needed. Overall, OpenERP provides a versatile and powerful solution for businesses looking to enhance their operations and improve efficiency.
Implementation and Setup
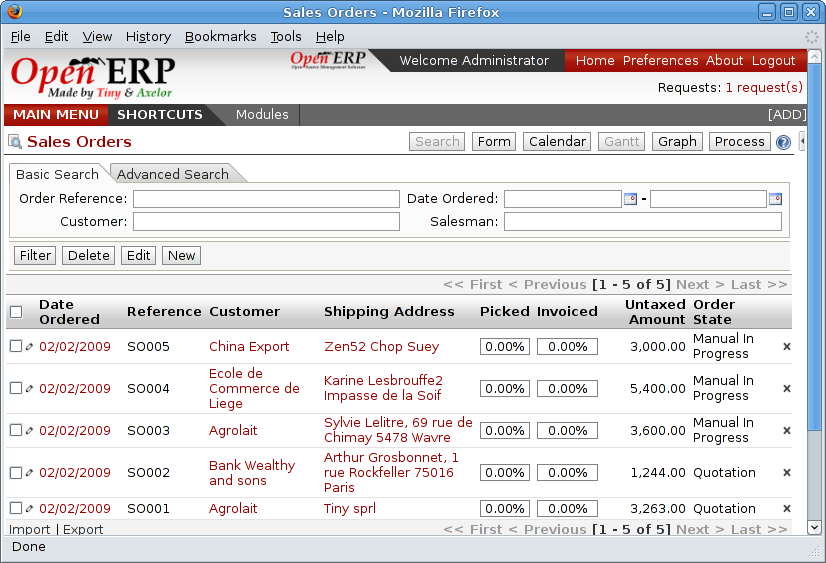
Implementing OpenERP involves a series of systematic steps to ensure a successful installation and configuration of the software. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the necessary system requirements and a step-by-step approach to set up OpenERP effectively.
System Requirements for OpenERP Installation
Before diving into the installation process, it is crucial to understand the system requirements to ensure optimal performance. The following specifications are recommended for an efficient OpenERP setup:
- Operating System: Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Debian, or CentOS are preferred.
- Processor: A dual-core CPU or higher is recommended for better performance.
- RAM: Minimum of 2 GB RAM; 4 GB or more is ideal for larger databases.
- Disk Space: At least 20 GB of free disk space for installation and data storage.
- Database: PostgreSQL version 9.5 or later is required for managing the OpenERP database.
- Dependencies: Python 2.7 or later, along with required libraries including libxml2, libxslt, and others as specified in the OpenERP documentation.
Step-by-Step Guide for Installing OpenERP
Installing OpenERP requires attention to detail at each step to ensure a smooth process. Below is a structured guide detailing each phase of the installation:
- Update System Packages: Always start by updating your system’s package list. Use the command:
sudo apt-get update
- Install Required Dependencies: Install necessary packages by running:
sudo apt-get install python-pip build-essential libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev zlib1g-dev libsasl2-dev libldap2-dev
- Install PostgreSQL: Install PostgreSQL with the command:
sudo apt-get install postgresql
- Create PostgreSQL User: Set up a user for OpenERP in PostgreSQL:
sudo -u postgres createuser –createdb –username postgres –pwprompt openerp
- Download OpenERP: Fetch the latest version of OpenERP from the official repository:
git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo –depth 1 –branch master –single-branch
- Install Python Packages: Navigate to the downloaded OpenERP directory and install the required Python packages:
cd odoo && pip install -r requirements.txt
- Configure OpenERP: Create a configuration file and edit for your setup. Use:
sudo nano /etc/openerp-server.conf
Customize it with your database name and user credentials.
- Start OpenERP Server: Run OpenERP by executing:
python openerp-server –config=/etc/openerp-server.conf
Initial Configuration Settings for OpenERP Instance
Once OpenERP is installed, initial configuration is necessary to tailor the system to your business needs. Key settings to configure include:
- Database Configuration: Ensure that the database name, user, and password match the details you previously set.
- Server Actions: Set parameters such as server time zone, language, and currency to align with your operational requirements.
- Modules Installation: Decide on which modules to install that best suit your business processes, such as Sales, Inventory, and Accounting.
- User Roles and Permissions: Establish access rights for different user roles to maintain security and operational integrity.
Modules and Customization
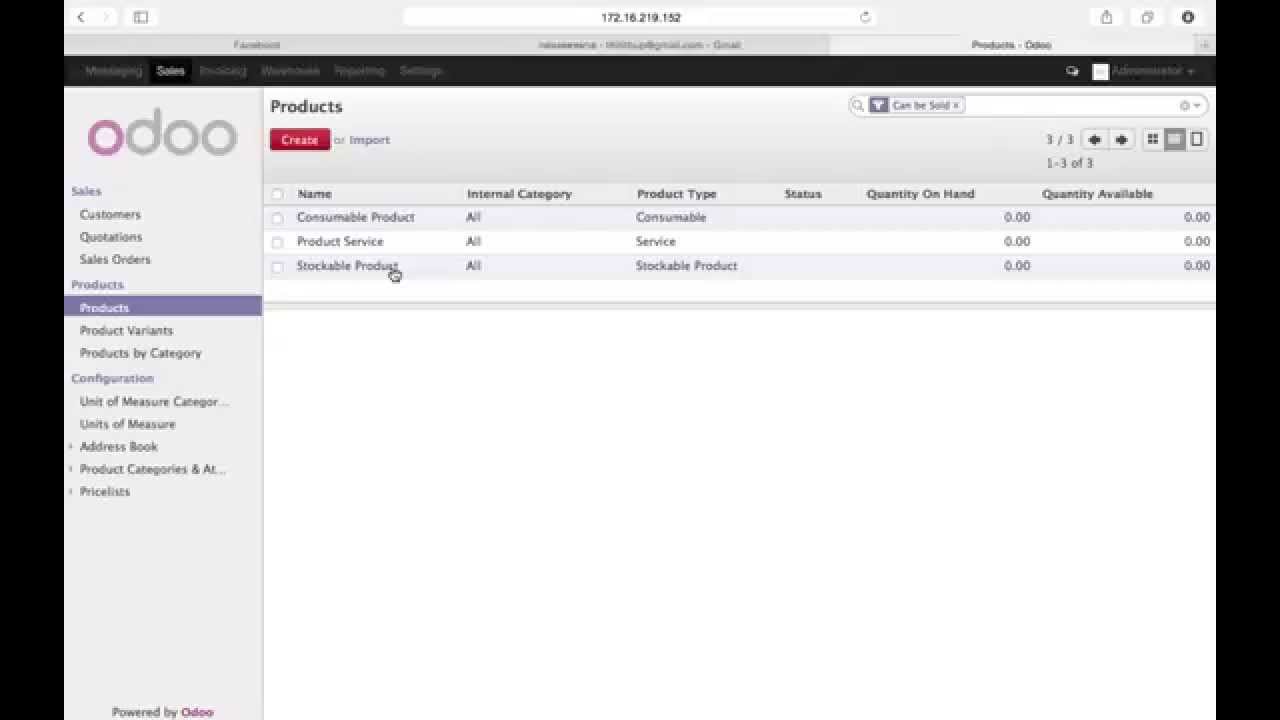
OpenERP, now known as Odoo, is equipped with a robust ecosystem of modules that enhance its functionality, allowing businesses to tailor the software to their specific needs. The modular architecture of OpenERP enables users to pick and choose the components that best align with their operational requirements. Customization further amplifies this flexibility, empowering developers to create bespoke modules that address unique business challenges. This segment focuses on the most popular modules, the development of custom modules, and methods for integrating OpenERP with other software solutions.
Popular Modules for OpenERP
OpenERP boasts a diverse range of modules that cater to various business functions. Understanding the most utilized modules can help organizations optimize their operations. Below are some of the key modules frequently recognized for their effectiveness:
- Sales Management: This module streamlines the sales process, enabling businesses to manage leads, quotations, and orders efficiently.
- Inventory Management: It provides robust tools for tracking stock levels, managing suppliers, and fulfilling customer orders, ensuring optimal inventory control.
- Accounting: This core module simplifies financial management with features for invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): It aids businesses in managing customer interactions, improving lead tracking, and enhancing sales pipeline visibility.
- Human Resources: This module assists in managing employee records, payroll, and recruitment processes, facilitating efficient HR management.
- Project Management: It provides tools for planning, tracking project tasks, and resource management, helping teams deliver on time and stay within budget.
Development of Custom Modules for OpenERP
Creating custom modules in OpenERP allows businesses to implement solutions that are specifically tailored to their needs. The development process involves several key steps:
1. Setting Up the Development Environment: Developers must set up a suitable environment with access to OpenERP’s technical documentation and development tools.
2. Module Structure: A custom module is typically organized into a specific directory structure, including key files such as __manifest__.py, models, views, and security files. This structure defines the module’s metadata, business logic, and user interface.
3. Defining Models and Views: Developers create models to represent business objects within the module and define views for data entry and interaction. Python is used to write the business logic, while XML is employed for designing views.
4. Testing the Module: Rigorous testing is crucial to ensure that the module functions correctly and meets business requirements. Using OpenERP’s testing framework helps catch issues early in the development cycle.
5. Deployment: Once the module is tested and validated, it can be deployed in the OpenERP environment. Continuous updates and maintenance are necessary to adapt to changing business needs.
Custom modules can significantly enhance OpenERP’s capabilities, providing businesses with a competitive edge.
Integration of OpenERP with Other Software Solutions
Integrating OpenERP with other software solutions ensures seamless data flow and enhances overall business efficiency. There are several methods to achieve this integration:
– API Integration: OpenERP provides a comprehensive RESTful API that allows third-party applications to interact with its modules. This method enables real-time data exchange and functionality extension.
– Middleware Solutions: Tools such as Zapier or MuleSoft can bridge OpenERP and other systems, allowing for automated workflows that connect disparate applications without extensive coding.
– Database-level Integration: Direct integration at the database level can be employed for legacy systems where data can be synchronized via database queries. However, this approach requires careful management to avoid data inconsistency.
– Webhooks: Implementing webhooks allows OpenERP to send real-time notifications to other applications based on specific triggers, enabling instant data synchronization and updates.
Utilizing these integration methods can enhance operational agility and ensure that OpenERP works harmoniously with existing systems, driving efficiency and productivity.
User Experience and Support: Openerp
OpenERP, now known as Odoo, is designed with user experience at its core, ensuring that businesses can efficiently navigate its features. The user interface is intuitive, enabling users to quickly adapt and find the functionalities necessary for their operations. This aspect is critical in maximizing productivity and minimizing the learning curve associated with new software.
User Interface Design and Usability
The user interface of OpenERP is built on a modern framework that emphasizes clarity and ease of use. Its layout is organized into modules, allowing users to focus on specific business areas without overwhelming distractions. Key features that enhance usability include:
- Dashboard Customization: Users can personalize their dashboards to display metrics and functionalities that are most relevant to their roles.
- Intuitive Navigation: The sidebar menu categorizes different modules, making it straightforward for users to switch between various tasks.
- Responsive Design: OpenERP’s interface is responsive, ensuring optimal performance across devices, whether on desktops, tablets, or mobile phones.
The simplicity of the design and the accessibility of features contribute significantly to a positive user experience, reducing the time required for training and increasing overall satisfaction.
User Training Recommendations
Effective training is pivotal for maximizing the utility of OpenERP within an organization. Tailored training programs can equip users with the necessary skills to utilize all functionalities effectively. Consider the following recommendations for training users on OpenERP:
- Hands-On Workshops: Conduct interactive workshops that allow users to engage directly with the software, practicing real-life scenarios they will encounter in their daily tasks.
- Comprehensive User Manuals: Provide clear and concise user manuals that Artikel step-by-step processes for common tasks, serving as a reference guide.
- Online Tutorials and Webinars: Utilize multimedia resources such as video tutorials and webinars that users can access at their convenience, reinforcing their learning experience.
These training modalities not only enhance user competence but also empower staff to leverage the full potential of OpenERP.
Community Support and Resources
OpenERP has fostered a vibrant community that serves as a valuable resource for users. This community support is crucial for problem-solving and knowledge sharing. Key components of community support include:
- Online Forums and Discussion Boards: Platforms where users can ask questions, share experiences, and offer solutions, creating a collaborative learning environment.
- Documentation and Knowledge Base: Comprehensive documentation is available, detailing various features, installation processes, and troubleshooting tips.
- Third-Party Extensions: The community actively develops add-ons and modules that extend the functionality of OpenERP, which can be easily integrated based on specific business needs.
By engaging with the community, users can gain insights and solutions that are not always available through official channels, enhancing their overall experience with the software.
Question Bank
What is Openerp?
Openerp is an open-source enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that helps organizations manage various business processes in a unified system.
Is Openerp customizable?
Yes, Openerp is highly customizable, allowing users to develop and integrate modules to tailor the software to their specific needs.
What are the system requirements for Openerp?
The system requirements for Openerp typically include a compatible operating system, sufficient RAM and storage, and a database management system like PostgreSQL.
How can I get support for Openerp?
Support for Openerp can be accessed through community forums, online documentation, and various training resources available on the official website.
What modules are available for Openerp?
Openerp offers a wide range of modules, including those for accounting, inventory management, project management, and customer relationship management, among others.