rtklib kicks off our exploration into the world of GNSS, showcasing its remarkable capabilities and pivotal role in the advancement of positioning technology. As an open-source program, RTKLIB stands out for its versatility and efficiency in real-time kinematic positioning, enabling users to achieve centimeter-level accuracy, making it a game-changer for numerous applications.
With its rich history tracing back to its inception, RTKLIB has evolved significantly and continues to be integral in various industries, from agriculture to autonomous vehicles. Understanding its core functions, installation procedures, and data processing techniques is essential for harnessing the full potential of this powerful tool.
Overview of RTKLIB
RTKLIB is an open-source software package designed for high-precision GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) applications. It comprises a set of programs and libraries that facilitate the processing of GNSS data, enabling users to achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy. RTKLIB supports a wide range of GNSS systems, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, making it a versatile tool in geospatial fields.
The development of RTKLIB began in the early 2000s by Tomoji Takasu, who aimed to create a comprehensive GNSS toolkit that would be accessible to both researchers and practitioners. Over the years, RTKLIB has evolved significantly, incorporating advancements in GNSS technology and processing methods. Its significance lies in its ability to process real-time kinematic (RTK) and post-processing data, which are critical for various applications in surveying, agriculture, and autonomous navigation.
Main Functions and Features
RTKLIB offers an array of functions and features that cater to various GNSS processing needs. These include:
- Real-Time Kinematic Processing: RTKLIB enables real-time data processing, providing immediate feedback on positioning accuracy, which is vital for applications such as surveying and autonomous vehicle navigation.
- Post-Processing Capabilities: Users can process recorded GNSS data files with high precision, making it suitable for applications where real-time processing is not critical.
- Support for Multiple GNSS Systems: The software supports various GNSS constellations, enhancing its usability across different regions and improving accuracy and reliability.
- Motion Processing: RTKLIB can handle dynamic positioning, allowing for applications involving moving receivers, such as in marine or aerial contexts.
- Versatile Data Formats: It accommodates a variety of input data formats, enabling integration with different GNSS receivers and systems.
History and Development
RTKLIB’s journey started in 2003 when Tomoji Takasu initiated its development to provide a free and open-source solution for GNSS data processing. The project gained traction in academic and professional circles, leading to a community of users who contributed to its ongoing enhancement. Throughout its development, RTKLIB has incorporated numerous algorithms and methodologies to improve the accuracy and efficiency of GNSS processing.
The software has undergone multiple iterations, each introducing new functionalities and support for emerging GNSS technologies. Its open-source nature has played a significant role in fostering collaboration among developers and users, resulting in a robust platform that adapts to the rapidly changing landscape of GNSS applications.
Applications of RTKLIB
RTKLIB finds extensive use across various sectors, contributing significantly to modern technological advancements. Its applications include:
- Surveying: Surveyors utilize RTKLIB for high-precision land measurements, boundary determinations, and construction site layouts.
- Agriculture: In precision farming, RTKLIB aids in accurate field mapping, enabling farmers to optimize planting, fertilization, and harvesting processes.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The software supports navigation systems in self-driving cars, ensuring accurate positioning and enhancing safety.
- Mapping and GIS: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) professionals leverage RTKLIB for creating detailed and accurate maps, crucial for city planning and environmental monitoring.
- Drone Operations: Drones equipped with RTKLIB can achieve high positional accuracy, essential for aerial surveying and monitoring applications.
“RTKLIB has transformed the way we approach GNSS data processing, making high-accuracy positioning accessible to a broader audience.” – Tomoji Takasu
Installation and Setup
Installing RTKLIB is a crucial step for utilizing its powerful capabilities in processing GNSS data. The installation process varies depending on the operating system, but the essential components remain the same across platforms. Proper setup is essential for maximizing the software’s performance and ensuring a smooth experience with GNSS data processing.
Installation on Windows
For Windows users, follow these steps to install RTKLIB effectively:
- Visit the official RTKLIB website to download the latest version.
- Extract the downloaded ZIP file to your preferred directory, such as C:\RTKLIB.
- Ensure you have Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable installed, as it is required to run RTKLIB.
- Run the executable file
rtkrcv.exefrom the extracted folder to start the application. - Configure the application by setting paths for your GNSS data files and necessary parameters.
To enhance performance, consider allocating sufficient memory and CPU resources to RTKLIB, especially when processing large datasets.
Installation on Linux
The installation process on Linux involves compiling the source code:
- Open a terminal and install necessary dependencies using your package manager. Common packages include
gcc,g++,make, andlibboost-all-dev. - Clone the RTKLIB repository from GitHub using
git clone https://github.com/tomojitakasu/RTKLIB.git. - Navigate to the RTKLIB directory and run
maketo compile the binaries. - Once compiled, execute
./bin/rtkrcvto start the application. - Modify configuration files according to your data processing requirements.
For optimal performance, ensure your Linux system uses a real-time kernel, which can provide better responsiveness in data processing tasks.
Installation on macOS
Installing RTKLIB on macOS can be done by following these steps:
- Download the latest RTKLIB version from the official site.
- Extract the ZIP file and open the terminal.
- Navigate to the extracted folder and run
maketo compile the software. - Launch RTKLIB by executing
./bin/rtkrcv. - Adjust configuration files for GNSS data processing as needed.
Utilizing Homebrew can simplify the installation of dependencies, ensuring a smooth setup process.
Configuration Tips for Optimal Performance
Configuring RTKLIB correctly can significantly impact its performance and efficiency. Consider the following recommendations:
- Adjust the sampling rates of your GNSS receiver to align with RTKLIB’s processing capabilities.
- Optimize the input file formats; while RTKLIB supports various formats, using the native format can reduce processing overhead.
- Tune the algorithm settings based on your specific application scenarios, such as static or kinematic positioning.
- Ensure your antenna settings are correct; incorrect settings can lead to inaccurate results.
These configuration adjustments facilitate smoother operations and improved data processing outcomes.
Troubleshooting Installation Issues
Common installation issues can arise during the setup of RTKLIB, and having a checklist can help identify and resolve these problems quickly:
- Check that all dependencies are installed correctly, especially development libraries.
- Verify that the correct version of RTKLIB is downloaded for your operating system.
- Ensure proper permissions are set for executing binaries, especially on Linux and macOS.
- Consult the RTKLIB user manual for specific error messages that may arise during installation.
- Seek support from forums or user communities if issues persist.
This troubleshooting checklist can enhance the installation experience and help in achieving a successful setup of RTKLIB.
Data Processing Techniques
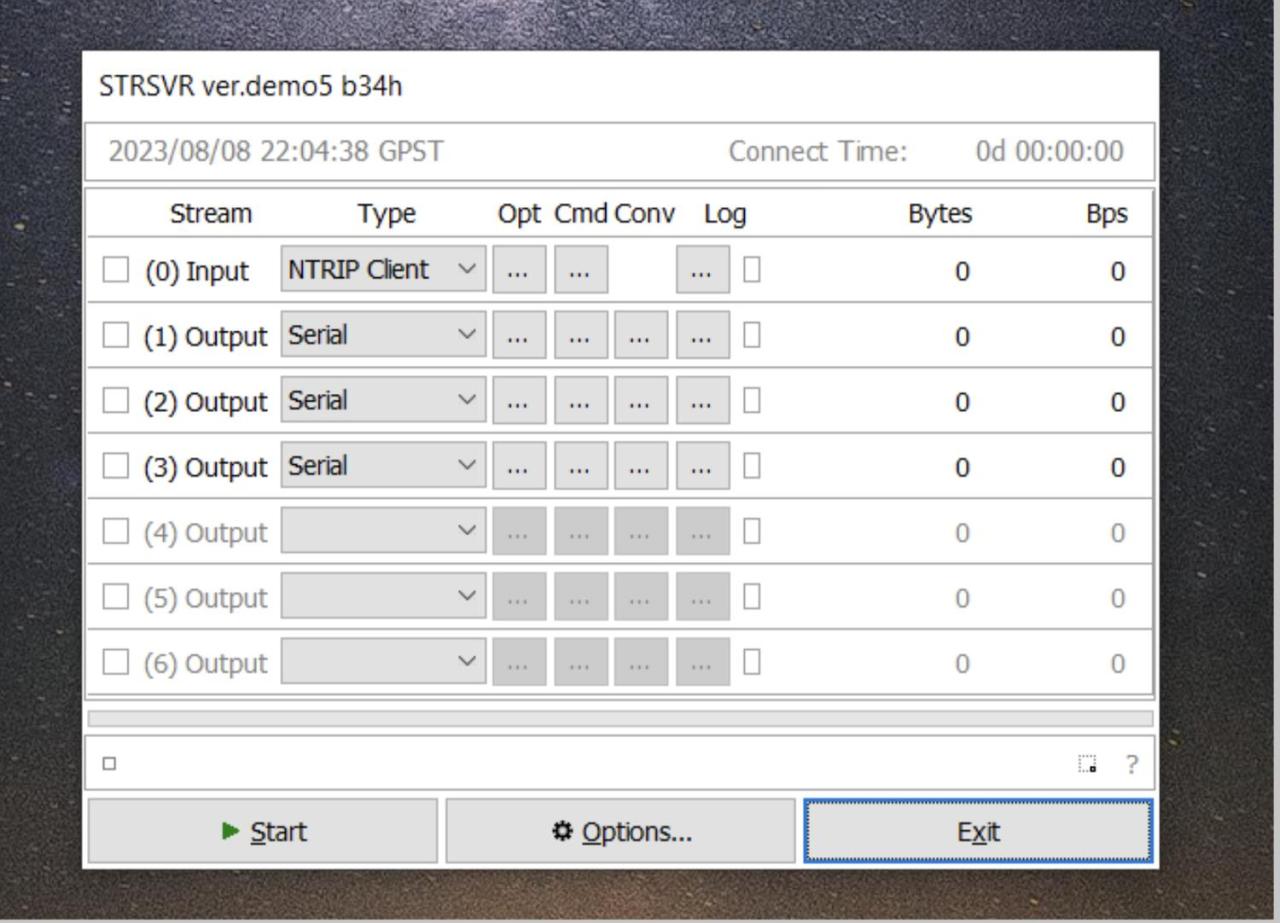
RTKLIB offers various data processing techniques that enable users to analyze GNSS data efficiently. The flexibility of these techniques allows for precise positioning and navigation, catering to different requirements and scenarios. Understanding the available processing modes and methodologies is crucial for users aiming to optimize their GNSS data processing workflows.
Data Processing Modes in RTKLIB
RTKLIB provides several processing modes, each tailored to specific use cases. These modes include:
- Static Mode: Suitable for applications where the GNSS receiver is stationary during data collection. This mode allows for high-accuracy positioning over longer durations.
- Kinematic Mode: Ideal for moving applications, where the receiver collects data while in motion. This mode is particularly useful for surveying and mapping tasks.
- Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Mode: Enables real-time data processing by using correction signals from a reference station, providing centimeter-level accuracy almost instantaneously.
- Post-Processing Mode: Involves collecting GNSS data and processing it later. This method is beneficial in scenarios where immediate data results are not critical, allowing for thorough analysis.
Methodologies for Processing GNSS Data, Rtklib
Processing GNSS data in RTKLIB involves several systematic steps that enhance the accuracy and reliability of the results. The key methodologies include:
- Data Collection: Gathering raw GNSS observations from receivers. This data forms the foundation for any subsequent analysis and must be collected under optimal conditions.
- Data Cleaning: Filtering out erroneous data points that may arise from multipath effects, atmospheric interference, or receiver errors. This step is essential to ensure data integrity.
- Estimation Algorithms: Utilizing various algorithms, such as Least Squares Estimation, to compute the most probable position by minimizing errors in the collected data.
- Adjustment and Correction: Applying corrections for satellite orbits, clock errors, and atmospheric conditions to refine the positioning results further.
Visualization of Processed Data
Visualizing processed GNSS data is vital for interpreting results and making informed decisions. RTKLIB offers tools that enable effective data representation. The following techniques are commonly used for visualization:
- RTKPlot: A graphical tool within RTKLIB that displays the positioning data over time. It provides users with visual feedback on the accuracy and consistency of the GNSS signals received.
- 3D Visualization: Users can generate 3D models of the surveyed area, which helps in better understanding spatial relationships and features in the environment.
- Graphs and Charts: RTKLIB allows for the creation of various graphs, such as position error plots, which help users assess the performance of their GNSS setup.
The ability to visualize GNSS data effectively enhances users’ understanding of their positioning accuracy and the overall performance of their data collection efforts.
Advanced Features and Customization
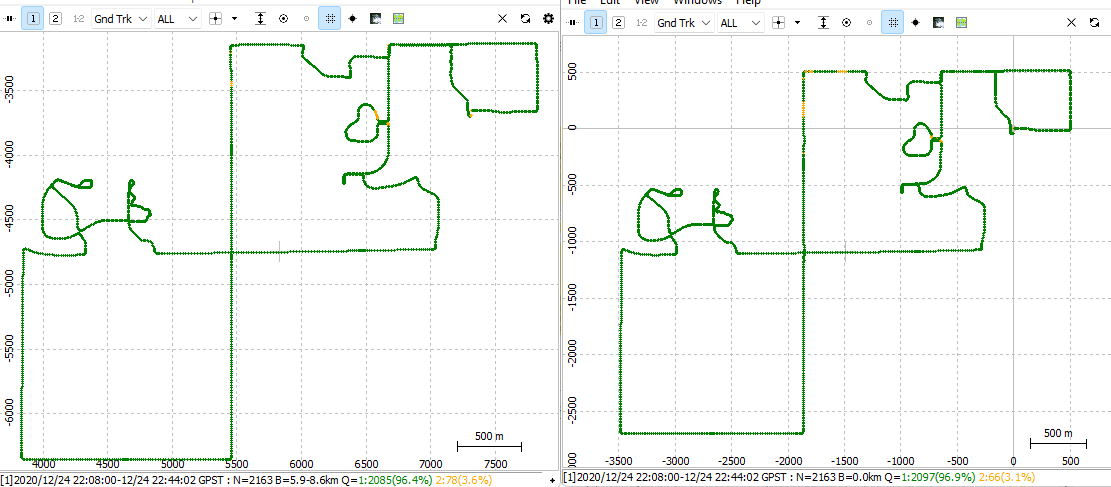
RTKLIB, a highly flexible and open-source software suite for GNSS data processing, offers a range of advanced features and customization options. These functionalities enable users to optimize their positioning solutions for specific requirements and improve their overall workflow. By leveraging these advanced capabilities, users can effectively address unique challenges in satellite-based positioning and navigation.
Advanced Data Processing Features
RTKLIB supports a variety of advanced data processing techniques that enhance the accuracy and reliability of GNSS solutions. These features allow users to refine their data interpretation and make informed decisions based on advanced algorithms and models.
- Precise Point Positioning (PPP): RTKLIB implements PPP techniques that utilize precise satellite orbit and clock information, enabling users to achieve centimeter-level accuracy without requiring a base station.
- Multi-constellation Support: The software can process signals from various GNSS constellations, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, providing flexibility and improved availability of signals.
- Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Processing: RTKLIB excels in real-time applications, allowing users to obtain instantaneous positions with high precision through the use of differential corrections.
- Static and Kinematic Processing Modes: RTKLIB accommodates both static and dynamic positioning scenarios, enabling users to select the most suitable mode based on their application needs.
Customization Options in RTKLIB
RTKLIB’s architecture facilitates extensive customization, allowing users to tailor the software to meet their individual requirements. This flexibility is essential for users who need to adapt RTKLIB for specialized tasks or integrate it with existing systems.
- Configurable Processing Parameters: Users can modify various processing parameters, such as measurement noise models, ambiguity resolution strategies, and output formats, to suit their specific GNSS processing needs.
- Custom Scripts and Modules: RTKLIB supports the integration of custom scripts and modules that can enhance or alter its functionalities, making it easier to implement specialized processing pipelines.
- User-defined Data Inputs and Outputs: RTKLIB allows users to define their own data input and output formats, facilitating seamless integration with other software tools or hardware systems.
Integration with Other Software and Hardware
The ability to integrate RTKLIB with other software and hardware systems is crucial for maximizing its utility in various applications. This interoperability enables users to create comprehensive solutions that leverage the strengths of multiple platforms.
- Integration with GIS Software: RTKLIB can be combined with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to enhance spatial data analysis and visualization. By exporting processed GNSS data to GIS platforms, users can perform sophisticated mapping and spatial analysis.
- Hardware Compatibility: RTKLIB supports a range of GNSS receivers and sensors, allowing users to connect their devices seamlessly. This compatibility ensures that users can leverage existing hardware without needing to switch to different solutions.
- Data Export to Other Processing Tools: The software can export processed data in standard formats (such as RINEX), enabling users to utilize other third-party processing tools for further analysis or visualization.
“The ability to customize RTKLIB makes it an invaluable tool for professionals seeking to implement tailored GNSS solutions in diverse environments.”
Question & Answer Hub: Rtklib
What is RTKLIB used for?
RTKLIB is used for real-time kinematic positioning and GNSS data processing, providing high-precision positioning solutions.
Is RTKLIB free to use?
Yes, RTKLIB is open-source software, which means it is free to use and modify.
What operating systems support RTKLIB?
RTKLIB supports various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Can RTKLIB be integrated with other software?
Yes, RTKLIB can be integrated with different software and hardware systems for enhanced functionality.
What are the common applications of RTKLIB?
Common applications include surveying, agriculture, robotics, and autonomous vehicle navigation.