sap2000 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This innovative software has transformed the landscape of structural engineering, enabling professionals to conduct complex analyses and designs with unparalleled ease. From its inception, SAP2000 has become synonymous with reliability and efficiency, widely adopted for various applications ranging from bridges to skyscrapers, demonstrating its versatility in modern engineering.
Introduction to SAP2000
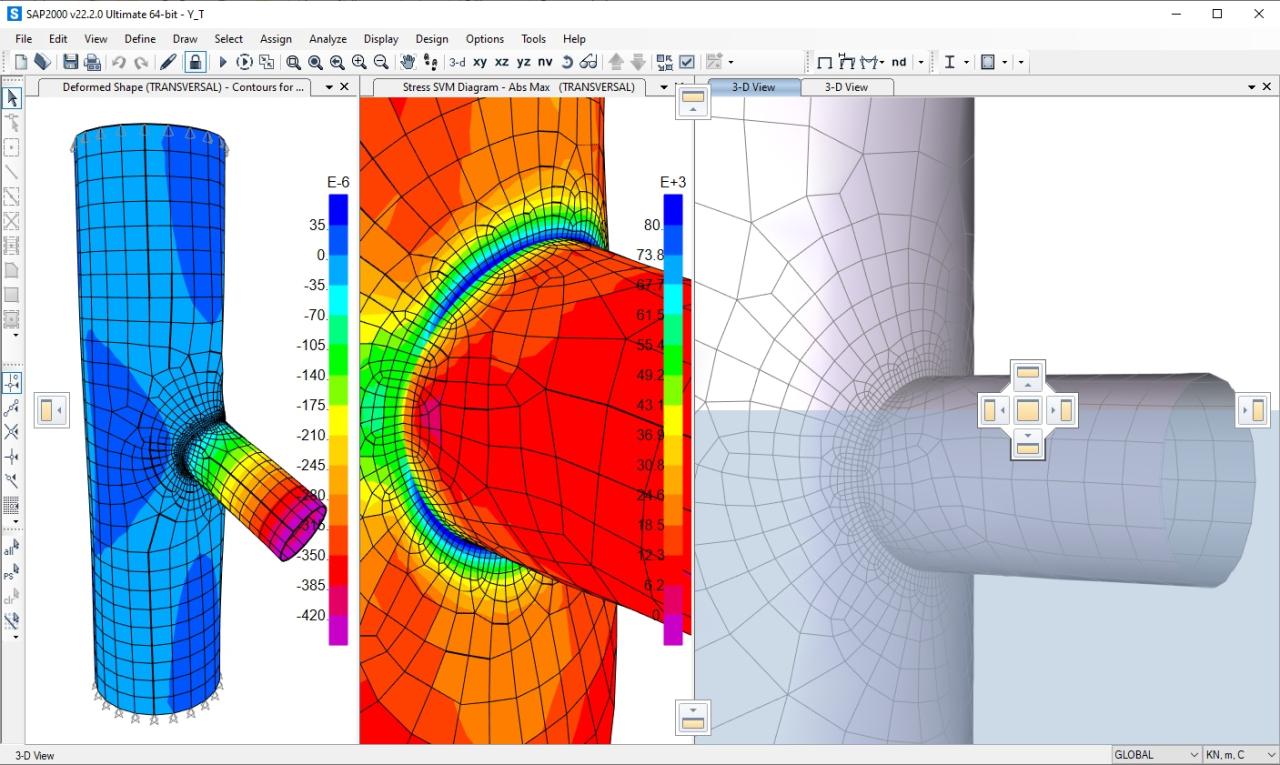
SAP2000 is a widely used structural analysis and design software application that plays a pivotal role in the engineering field. Its primary purpose is to facilitate the analysis and design of a broad range of structures, ensuring they meet safety and performance standards. Engineers leverage SAP2000 for both linear and nonlinear analysis, allowing for comprehensive evaluations of structural integrity under various load conditions.
SAP2000 has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1970s, originally developed by Computers and Structures, Inc. (CSI). Over the decades, it has become a benchmark in structural engineering software, integrating advanced computational methods and user-friendly interfaces. Its historical development showcases its significance in addressing complex structural challenges, adapting to modern engineering needs, and incorporating state-of-the-art features such as dynamic analysis and performance-based design.
Common Structures Analyzed with SAP2000
SAP2000 is versatile and applicable to a wide array of structures. The types of structures commonly analyzed using this software include:
- Buildings: SAP2000 is extensively utilized for high-rise buildings to ensure compliance with seismic and wind load regulations.
- Bridges: Structural engineers use SAP2000 to analyze various bridge configurations, including cantilever, arch, and suspension bridges, focusing on their dynamic responses.
- Towers: The software supports the design and analysis of telecommunication and utility towers, addressing stability and load management.
- Industrial Facilities: SAP2000 is suitable for analyzing complex industrial structures, including factories and warehouses, which often have unique loading scenarios.
- Dams: Engineers employ SAP2000 to study the stability and safety factors of dams under different environmental conditions and load applications.
The software’s capabilities allow for detailed modeling and simulation of these structures, making it an indispensable tool for engineers striving for innovation and safety in their designs. By utilizing SAP2000, professionals can optimize performance, enhance durability, and ensure that structures can withstand both anticipated and unforeseen loads.
Features and Functionalities of SAP2000
SAP2000 is a comprehensive structural analysis and design software solution that caters to a diverse range of engineering needs. Its robust features and functionalities enable engineers to create accurate models, perform complex analyses, and ensure compliance with various design codes across multiple disciplines. This section will delve into the primary capabilities of SAP2000, highlighting its advanced modeling tools, analysis methods, and supported design codes.
Modeling Capabilities
SAP2000 offers an intuitive interface and a variety of tools for effective modeling. Users can create detailed 3D models using a combination of geometric shapes, lines, and surfaces. This flexibility allows engineers to represent complex structures with ease. The key aspects of its modeling capabilities include:
- Graphical User Interface: The user-friendly GUI facilitates quick learning and efficient modeling, with drag-and-drop functionalities and interactive manipulation of elements.
- Import and Export Options: SAP2000 supports various file formats (e.g., DXF, IFC, and Revit) for seamless collaboration and integration with other software.
- Load Application: Users can define a wide range of loads, including dead loads, live loads, wind loads, and seismic loads, ensuring comprehensive analysis of structural behavior.
Analysis Options
The analytical capabilities of SAP2000 are extensive, providing engineers with the ability to conduct linear, non-linear, static, and dynamic analyses. Its advanced analysis options include:
- Linear Static Analysis: Facilitates the evaluation of structures under predictable load conditions, ensuring compliance with design standards.
- Dynamic Analysis: SAP2000 can perform response spectrum analysis, time history analysis, and modal analysis, essential for understanding the behavior of structures under dynamic loads, such as earthquakes.
- Non-linear Analysis: This feature allows for the assessment of material and geometric non-linearities, helping to predict real-world structural responses under extreme conditions.
Design Code Support, Sap2000
One of the key strengths of SAP2000 is its support for a wide range of design codes applicable to various engineering disciplines. This ensures that designs comply with local and international standards. The supported design codes include:
- AISC (American Institute of Steel Construction): Allows for steel design and analysis in accordance with the latest specifications.
- ACI (American Concrete Institute): Provides tools for reinforced concrete design, ensuring adherence to safety standards.
- Eurocode: Supports European design standards for structural engineering, covering a variety of materials.
- IBC (International Building Code): Ensures compliance with building regulations in various jurisdictions.
Advanced Functionalities
SAP2000 provides several advanced functionalities that enhance its analytical capabilities. These include:
- Dynamic Analysis: Features like modal response and time-history analysis can accurately predict how structures respond to dynamic loads, critical for earthquake engineering.
- Non-linear Modeling: Users can model complex material behaviors and geometric non-linearities, allowing for more accurate predictions of structural responses under adverse conditions.
- Performance-Based Design: This functionality enables engineers to design structures not only for safety but also for serviceability and sustainability, addressing modern engineering challenges.
“SAP2000 combines powerful modeling capabilities with versatile analysis options, making it a go-to tool for structural engineers worldwide.”
User Interface and Workflow
The SAP2000 user interface is designed to facilitate a seamless experience for engineers and designers working on various structural analysis and design projects. Its layout is intuitive, enabling users to navigate through tools and functionalities efficiently. Understanding the user interface and the typical workflow for modeling in SAP2000 is essential for maximizing productivity and minimizing errors.
The SAP2000 interface comprises several key components, including the main toolbar, menu bar, modeling area, and data input panels. The main toolbar provides quick access to frequently used tools, while the menu bar lists various commands organized by categories such as File, Edit, View, and Analysis. The modeling area, often referred to as the workspace, is where users create and visualize their models in both 2D and 3D formats. Data input panels allow users to define properties, loads, and boundary conditions, streamlining the modeling process.
Layout of the SAP2000 User Interface
The layout of the SAP2000 user interface is structured to enhance user interaction with the software. Key features of the layout include:
- Main Toolbar: Contains icons for essential functions such as file operations, drawing tools, and analysis commands, allowing for quick execution of common tasks.
- Menu Bar: Organized into dropdown menus categorizing options like File, Edit, Display, and Analysis, providing users with comprehensive access to the software’s capabilities.
- Modeling Area: This central space displays the model in progress, with options to toggle between 2D views and 3D visualizations, helping users to easily manipulate structures.
- Data Input Panels: Located typically on the right side, these panels allow users to input and modify properties, loads, and analysis settings without disrupting the modeling area.
Typical Workflow for Creating a Model in SAP2000
Creating a model in SAP2000 involves a systematic workflow that guides users from project initiation to analysis. The key steps in this workflow include:
- Project Setup: Initiate a new project by defining the project settings, including units, analysis type, and model preferences.
- Geometry Definition: Use drawing tools to create the structural geometry, including beams, columns, and slabs, either through manual input or by importing from CAD software.
- Property Assignment: Assign material and section properties to the structural elements, ensuring compliance with design standards and specifications.
- Load Application: Define and apply loads such as dead, live, wind, or seismic loads according to relevant guidelines and standards.
- Analysis Configuration: Set up analysis parameters, selecting the appropriate analysis type (linear, nonlinear, response spectrum, etc.) for the project’s requirements.
- Running Analysis: Execute the analysis and review the results generated by the software, identifying critical stress points and deformation patterns.
- Reporting and Output: Generate reports summarizing the analysis findings, including graphical representations and detailed calculations for documentation and review.
Shortcuts and Tips for Improving Efficiency
To enhance productivity while using SAP2000, familiarity with keyboard shortcuts and efficiency tips can be invaluable. Below is a compilation of useful shortcuts and strategies:
- Keyboard Shortcuts:
- Ctrl + N: Create a new model.
- Ctrl + O: Open an existing model.
- Ctrl + S: Save the current model.
- F1: Access help documentation.
- Navigation Tips:
- Use the mouse scroll wheel to zoom in and out of the modeling area for better visualization of details.
- Right-clicking on elements provides contextual menus for quick access to editing options.
- Model Organization:
- Group similar elements using the ‘Groups’ feature for easier management and analysis.
- Utilize layers to separate different components of the model, enhancing clarity during complex designs.
Utilizing these shortcuts and tips can significantly reduce modeling time, allowing engineers to focus more on design and analysis rather than repetitive tasks.
Practical Applications and Examples
SAP2000 is widely recognized for its versatility and robustness in structural engineering and design. The software is employed across various industries, including civil engineering, architecture, and construction, making it essential for professionals working on complex projects. This section delves into real-world applications of SAP2000, illustrating its practical use through case studies and addressing common challenges encountered during its operation, alongside effective solutions.
Case Study: High-Rise Building Analysis
A notable example of SAP2000’s application is the analysis and design of a high-rise building project in a seismic-prone region. The project involved a 40-story residential tower designed to withstand significant lateral forces due to earthquakes. Utilizing SAP2000, engineers performed the following steps:
1. Modeling the Structure: The building was modeled with precise geometric and material properties, including the use of reinforced concrete and dynamic loading conditions.
2. Load Analysis: Dead loads, live loads, wind loads, and seismic loads were applied based on relevant codes and standards, ensuring the model accurately reflected real-world conditions.
3. Dynamic Analysis: A response spectrum analysis was conducted to assess the building’s performance during seismic events, allowing engineers to evaluate its stability and resilience.
The results indicated that the design met all safety requirements while optimizing material usage, thereby enhancing sustainability.
Common Challenges and Overcoming Strategies
While SAP2000 is a powerful tool, users often face specific challenges. Understanding these issues and implementing strategic solutions is critical for successful project execution. Some common challenges include:
– Complex Model Setup: Creating detailed models can be time-consuming and may lead to errors. To mitigate this, users should:
– Utilize templates for recurring structural types.
– Employ automated features for generating load combinations.
– Interoperability Issues: Difficulty in importing and exporting data can disrupt workflow. To address this, it is recommended to:
– Familiarize with different file formats supported by SAP2000 such as .SAP, .DXF, and .CSV.
– Regularly update the software to ensure compatibility with other BIM tools.
– Debugging Analysis Errors: Users may encounter analysis errors that can be difficult to diagnose. Strategies include:
– Breaking down the model into smaller components to isolate issues.
– Consulting the extensive documentation and support forums provided by the SAP2000 community.
Data Exporting and Importing Processes
The ability to export and import data in SAP2000 enhances collaboration and improves efficiency. Understanding the formats and considerations involved is crucial for seamless data handling.
– Exporting Data: SAP2000 allows users to export models and results in various formats, including:
– SAP2000 format (.SAP): Best for complete project data transfer.
– DXF files: Useful for sharing geometrical data with CAD software.
– CSV files: Ideal for exporting tabular data such as material properties and load cases.
– Importing Data: Importing data into SAP2000 can also be executed through different formats. Key considerations include:
– Ensuring the accuracy of the imported model by verifying compatibility with SAP2000’s requirements.
– Using the import wizard to facilitate a structured process, making it easier to manage complex models imported from external sources.
By mastering the exporting and importing processes, users can significantly enhance their productivity and ensure a smoother workflow in their engineering projects.
Answers to Common Questions
What types of structures can be analyzed using SAP2000?
SAP2000 can analyze a wide range of structures including buildings, bridges, dams, and towers.
Is SAP2000 suitable for dynamic analysis?
Yes, SAP2000 supports dynamic analysis features, making it ideal for seismic and wind load evaluations.
Can I import models from other software into SAP2000?
Yes, SAP2000 allows data import from other software using various file formats for better interoperability.
What design codes are supported by SAP2000?
SAP2000 supports numerous design codes across different engineering disciplines including AISC, ACI, and Eurocodes.
Are there any specific hardware requirements for running SAP2000?
SAP2000 has recommended hardware requirements that include a modern multi-core processor, adequate RAM, and a compatible graphics card for optimal performance.